|
|
Additives
Amine Free
Antiblock
Antistat
Apparent Density
ASTM
|
Materials added to the extrusion process to change the characteristics or appearance of the film or bag. Common additives include: Color, slip, antistat, antiblock, UVI, UVA and VCI.
Antistat that is free from fatty acids.
A material that is either incorporated in the resin pellet or used as an additive to stop blocking the sticking of two surfaces.
An additive that is incorporated in the extrusion process to help reduce or eliminate the accumulation of a static charge.
The weight in air of a unit volume of material.
Acronym for the American Society for Testing and Materials.
|
|
|
Barefoot
Blocking
Blown film extrusion
Blow up ratio
Bottom seal
Bottom seal bag
Bulk density
|
Low density polyethylene (LDPE) or linear low density polyethylene (LLDPE) that is free from slip or antiblock additives causing the finished product to zero slip.
The tendency of sheets or films to stick together under light pressure making separation difficult. Blocking can be reduced by using anti-blocking agents.
The process in which resin pellets are melted through a circular die to form a thin tube. Air is introduced in the die which blows up the tube like a balloon. The hot film is then cooled with the help of cool air and is further flattened. The flattened film is then converted into bags or film.
The ratio of the diameter of the bubble to the die diameter in blown film extrusion.
A seal along the bottom of a bag opposite the open end.
A tubular style bag with a seal at the bottom opposite the open end. A bottom seal bag will not have side welds.
Weight per unit volume of material including voids which are inherent as tested.
|
|
|
Centerfold film
Co-extrusion
Colorant
Copolymer
|
Film folded in half and wound on a roll.
An extrusion process where two (or more) melt streams are combined in the die to make an extrudate of two (or more) layers of plastic. Often, one of the layers is a barrier layer.
Material added to impart color to the plastic usually a die or pigment.
A polymer of resin made by polymerizing two or more monomers together. The second is added to improve properties such as adhesion or impact.
|
|
|
Density
|
Mass per unit volume. See apparent density and bulk density.
|
|
|
Elongation
Extrusion
|
A test used to measure the amount film can stretch without breaking.
The process of making a product by forcing material through a die.
|
|
|
Fish eyes
Form-Fill-Seal
|
Defects in an extrudate (usually film) which look like the eyes of a fish. Fish eyes are caused by small particles of either un-melted or cross-linked resin. They are small masses that have not blended completely into the surrounding material.
A packaging process in which a film is formed into a container, filled and then sealed.
|

|
|
Gauge
Gauge bands
Gels
Gusset
|
The thickness of the material expressed in mils (thousandths of an inch).
Regions of increased thickness on a roll of film produced through winding thicker film in the same place or on the same part of the reel.
Lumps seen in film which result from resin degradation or cross-linking.
The folded-in portion of flattened tubular film or bags. Designed to increase the capacity of a bag.
|
|
|
Heat sealing
|
A technique used for sealing film by applying heat.
|
|
|
Impact strength
|
The force required to fracture polyethylene film under specified conditions of impact by a free falling dart.
|
|
|
Linear low density
Low density
|
Also known as LLDPE. A copolymer resin that is made by polymerizing ethylene with a small percent of a higher olefin such as butene, hexane, octane or metallocene. LLDPE resins combine ease of processing with low gels and good film strength.
Also known as LDPE. LDPE is ethylene that is manufactured under extreme heat and pressure. The ethylene molecules are linked in random fashion with the main chains having side branches. LDPE resins have moderate tensile strength which provides less strength and puncture resistance than LLDPE resins.
|
|
|
Plastic
Polyethylene
Polymer
Polymerization
Process ability
|
A material that contains, as an essential ingredient, one or more higher molecular weight polymers. It is generally solid at room temperature and is capable of flowing, under heat and pressure, to form a final shape.
Also known as PE. PE is a resin that is made from ethylene gas and used as a raw material in blown film extrusion.
A chemical compound made up of a large number of repeating molecular units.
The chemical process whereby a monomer is turned into a polymer or resin.
The ease with which a plastic material can be extruded.
|
|
|
Repro
|
Reprocessed plastic material made into pellets. Feedstock is mostly post industrial plastic that is ground into small regrind form and then pelletized.
|
|
|
Sheet
Shrinkage
Shrink film
Side seal
Single wound sheeting
Slip
Slit seal
Static decay
Surface resistivity
Static
|
An individual piece of sheeting.
The reduction in dimensions that a component suffers after production.
A plastic film which has been produced under special orientation and can be sealed around a product and shrunk by exposure to hot air.
Typically, an out-of-line converted bag with seals on the side and a folded bottom.
Also known as SWS. A single layer of plastic wound on a core.
A material incorporated into the resin pellets or added during extrusion to reduce friction of the film against itself or processing equipment.
A seal that is created when a tubular bag is slit (in the length direction) with an electronically controlled hot knife and sealed at the same time. This process produces more than one bag with slit seals out of one tubular bag.
The time required for a sample to dissipate a percentage (90-99%) of an initial electrical charge of 5kV (both positive and negative).
Measures the electrical resistance of the surface of the plastic.
The electrical charge generated, and retained, on insulated surfaces. Static is generated on film surfaces when they are separated.
|

|
|
Tensile strength
Transverse direction
Tubular bag
Tubular film
|
The resistance of a material to longitudinal (machine direction) tension stress. A measure in force in pounds per square inch required to break a strip of film of specified length, width and thickness.
Also known as TD. The direction across the extruder (i.e. right angles) to the machine direction.
A bag with no side seals or slit seals only a bottom seal.
Film produced by extrusion. A tube of softened plastic is inflated to the required diameter, cooled and collected on a reel.
|
|
|
Ultra Violet Inhibitor
Ultra Violet Absorber
|
Also known as UVI. UVI is an additive that is introduced during the extrusion process to prevent sunlight or UV damage to the film or bag.
Also known as UVA. UVA is an additive that is introduced during the extrusion process to protect the product inside the bag or film from sunlight or UV rays.
|
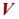
|
|
Vents
|
Small holes die punched into the film or bag to allow air to escape.
|

|
|
Yield
|
The amount of film at a given thickness produced from a given weight or resin.
|